What is SFTP ?
SFTP, or SSH File Transfer Protocol for short, is a much more secure way to move files. Using the SSH protocol, it supports encryption and other security methods used to better protect file transfers. It’s the only secure file transfer protocol that protects against attacks at any point in the data transfer process, making it the preferred protocol.
During file transfer, all of the data is divided into packets and sent through a single secure connection.
Sensitive information will be encrypted and made unreadable when being transferred between the client and the server. In other words, the original content (plaintext) will be replaced by an incoherent string of characters (ciphertext).
Only the recipient with the required decryption key will be able to see the original content. This prevents any unauthorized access during file transfer.
Regular file transfer protocol (FTP) has two different channels to exchange data — the command channel and the data channel. In contrast, SFTP has only one encrypted channel where the data is exchanged in encrypted, formatted packets
SFTP configure in RHEL/CentOS
Configure SFTP on Ubuntu Server
#sudo addgroup sftp
#sudo adduser sftpuser
#sudo usermod -aG sftp sftpuser
#sudo passwd sftpuser
#sudo chmod 700 /home/sftpuser
#sftp sftpuser@localhost
sfpt> mkdir sftp-data
#ls
#exit
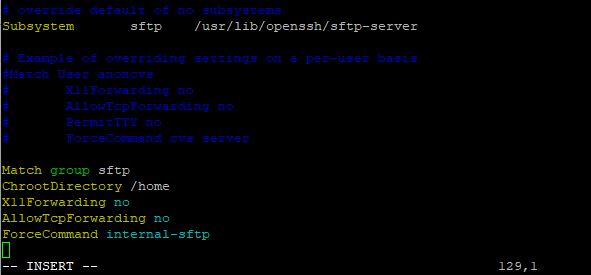
#sudo vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Go to last line and Do entry
Match group sftp
ChrootDircetory /home
X11Forwarding no
AllowTcpForwarding no
ForceCommand internal-sftp
Esc :wq! save and exit file
#sudo vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
change default port 22 to 7777
Restart the ssh service
#sudo /etc/init.d/ssh restart
Connect to filezilla





0 Comments